
Urinary Organs

Urinary Organ Objectives
-
List the urinary organs and state the function(s) of each organ.
- Describe the structure of a nephron and how it filters, reabsorbs, and secretes.
- Explain the important functions of the smooth muscle and transitional epithelial tissue in the bladder.
We are starting with an introduction to the organs of the urinary system.
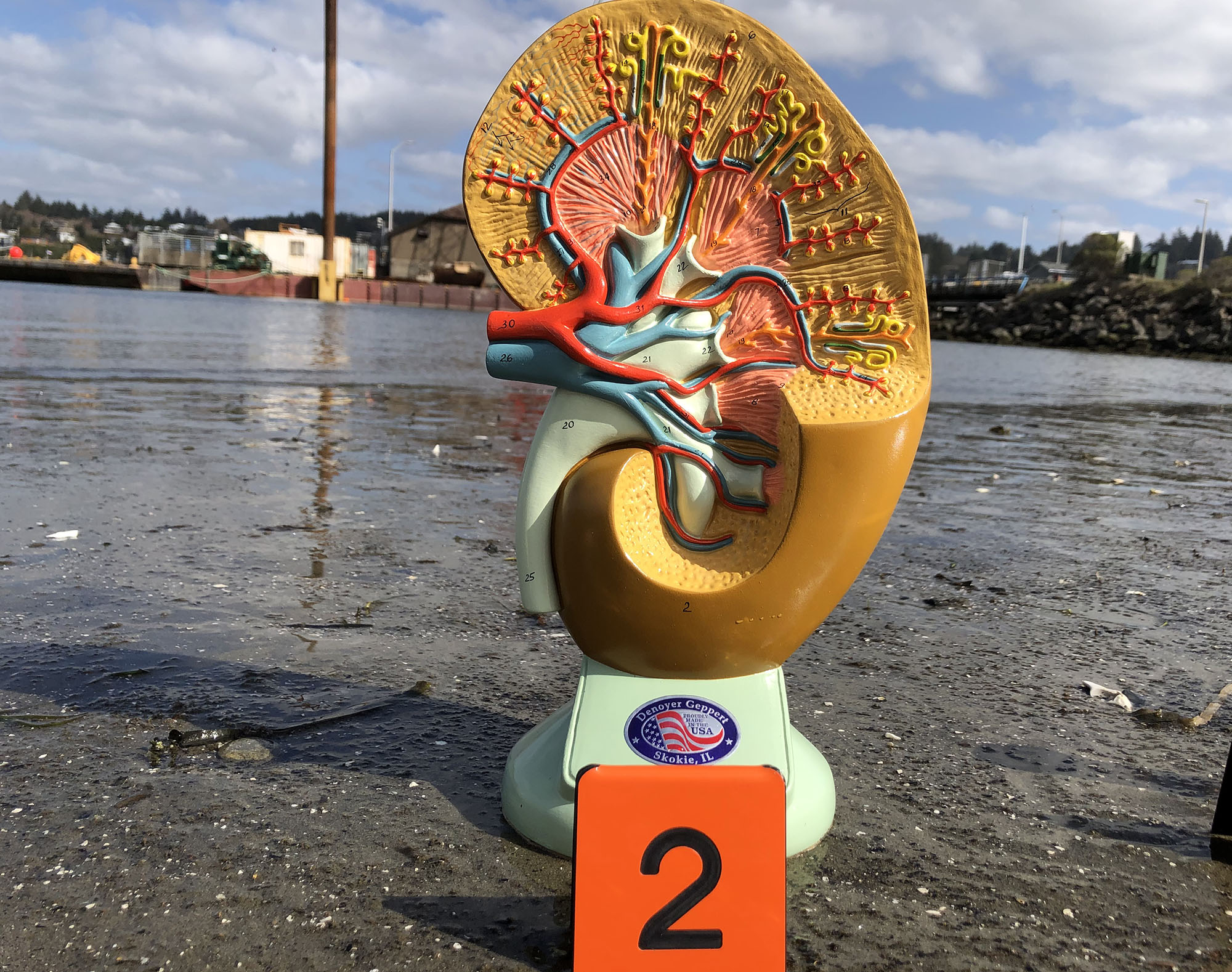
The poster and model in this video illustrate how significant the blood supply is to the kidneys and the amount of urea (along with other wastes) that is filtered out of the blood plasma.
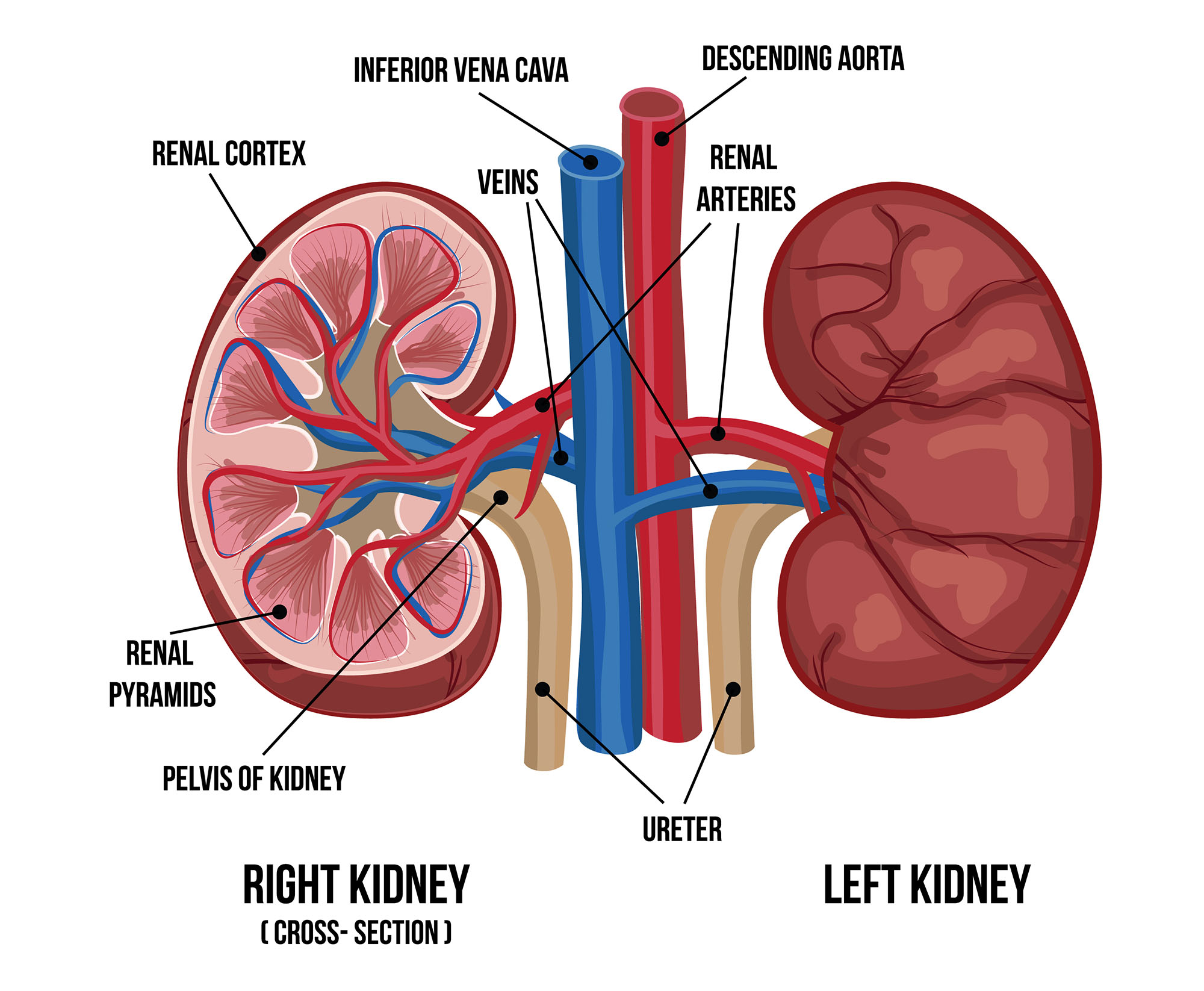
In the urinary system, most of the action is happening in the kidneys. Approximately a million nephrons in each kidney filter blood plasma and create urine.
Each nephron filters blood plasma, pulling out waste and excessive materials. This model shows the glomerulus of capillaries, as well as the tubule that enables reabsorption of needed materials back into the blood and secretion of urine.
Under the microscope we can see the glomeruli and a lot of tubules running in slightly different directions.
We can’t forget about the bladder, it has an incredible ability to stretch as it fills with urine.
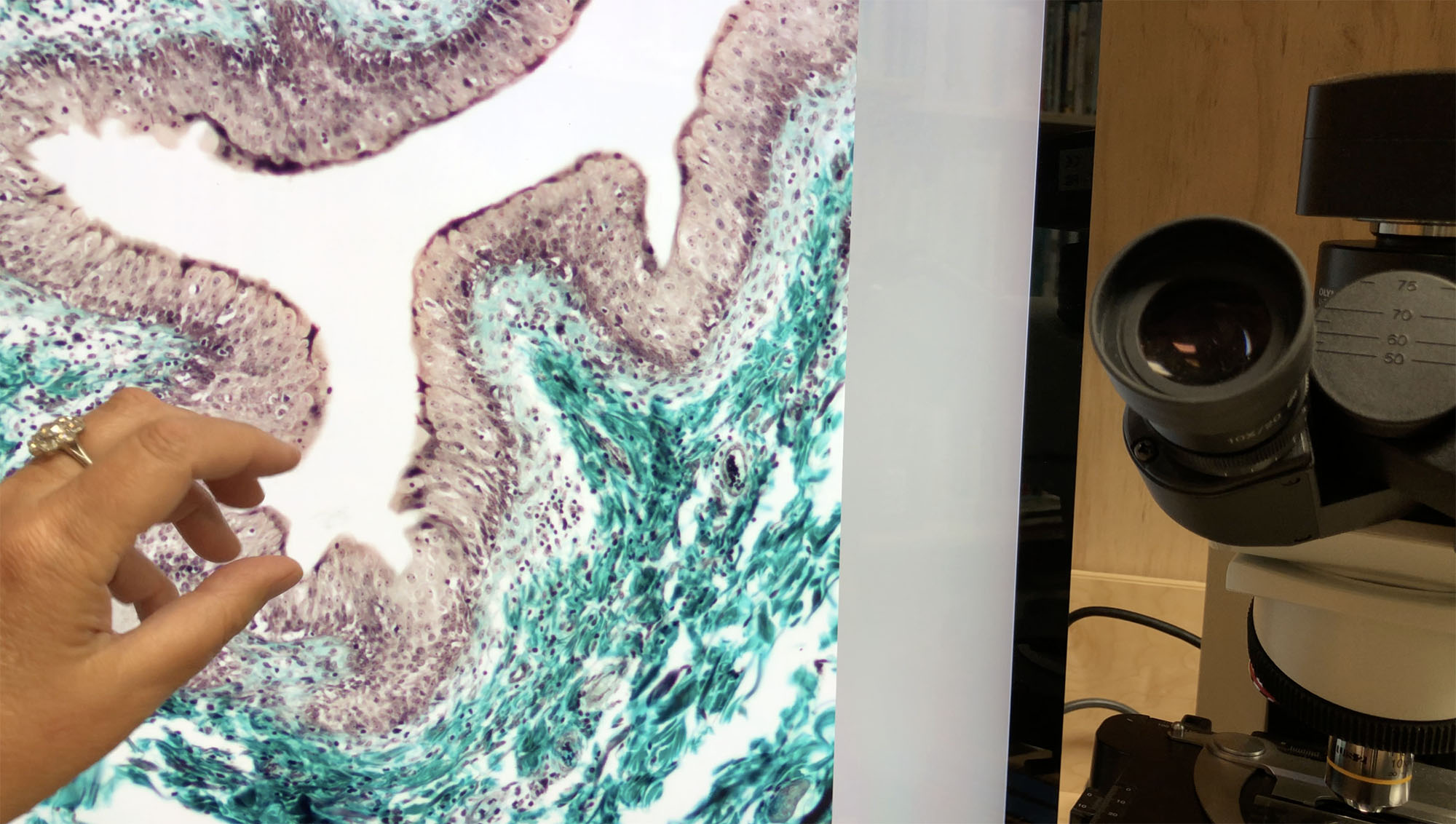
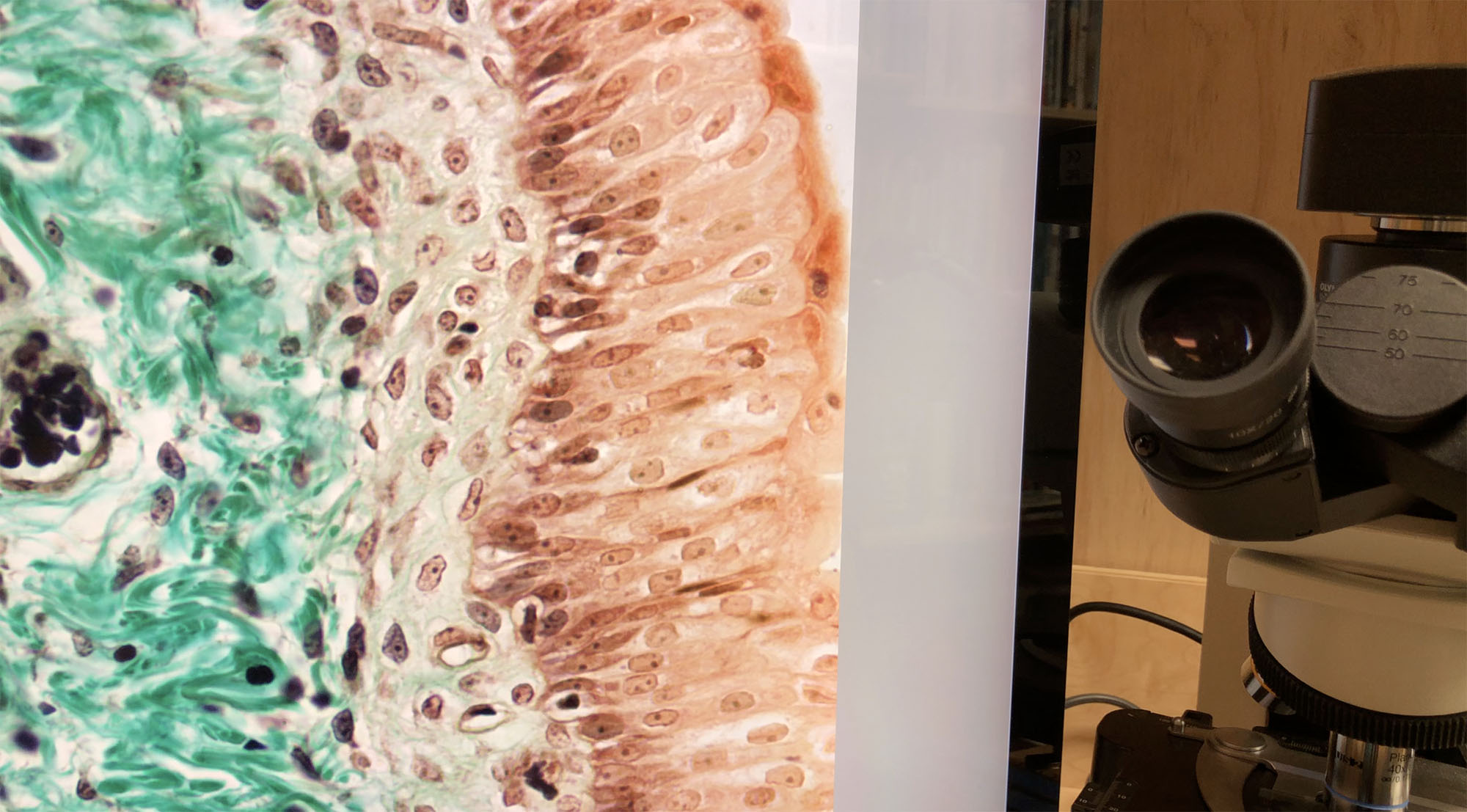
What gives human urine its characteristic yellow-ish color? ________What is the source of urea in urine? ________
Answer: broken down hemoglobin; toxic ammonia from cells is converted to less toxic urea by the liver
Which organ(s) actually filter the blood plasma? _____What are the names of the smaller units that do the filtering? _____ So much is filtered out, much of the water and ions need to be _____ into the blood plasma. Which tubes carry the urine to the bladder? _____ What is the name of the tube that carries urine out of the body? _____
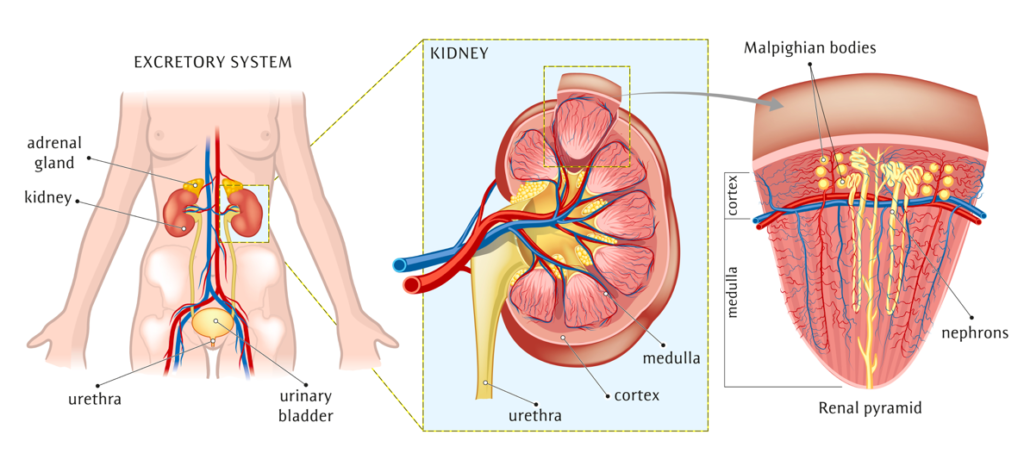
Answers: Kidneys; nephrons; reabsorbed; ureters; urethra
The next section provides an overview of urinalysis and urinary tract disorders.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
list the urinary organs and state the function(s) of each organ?
- describe the structure of a nephron and how it filters, reabsorbs, and secretes?
- explain the important functions of the smooth muscle and transitional epithelial tissue in the bladder?






